Supstanca P
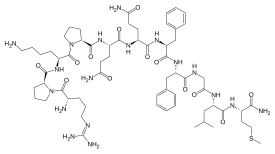
U neuronauci supstanca P (SP) je neuropeptid: undekapeptid koji funkcioniše kao neurotransmiter i neuromodulator.[5][6] Ovaj molekul pripada familiji tahikininskih neuropeptida. Supstanca P i njen blisko srodni neuropeptid neurokinin A (NKA) nastaju iz poliproteinskog prekurzora nakon diferencijalnog splajsovanja gena preprotahikinina A. Aminokiselinska sekvenca supstance P je[7][8]:
| Tahikinin, prekurzor 1 | |
|---|---|
| |
| Model supstance P | |
| Identifikatori | |
| Simbol | TAC1 |
| Alt. simboli | TAC2, NKNA |
| Entrez | 6863 |
| HUGO | 11517 |
| OMIM | 162320 |
| RefSeq | NM_003182 |
| UniProt | P20366 |
| Drugi podaci | |
| Lokus | Hromozom 7 q21-q22 |
| Supstanca P | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Identifikacija | |||
| CAS registarski broj | 33507-63-0 | ||
| PubChem[1][2] | 36511 | ||
| ChemSpider[3] | 33558 | ||
| MeSH | |||
| ChEMBL[4] | CHEMBL235363 | ||
| |||
| Svojstva | |||
| Molekulska formula | C63H98N18O13S | ||
| Molarna masa | 1347.63 g/mol | ||
|
Ukoliko nije drugačije napomenuto, podaci se odnose na standardno stanje (25 °C, 100 kPa) materijala | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Supstanca P se oslobađa iz završetaka specifičnih senzornih nerava. Nađena je u mozgu i kičmenoj moždini, i učestvuje u inflamatornim procesima i senzaciji bola.
Otkriće
urediSupstancu P su originalno otkrili 1931 Ulf von Euler i Džon H. Gadum kao extrakt tkiva koji izaziva intestinalne kontrakcije in vitro.[9] Njena distribucija u tkivu i biološka dejstva su detaljno ispitivana tokom decenija koje su sledele.[5] NKA (prethodno poznata kao supstanca K ili neuromedin L) je izolovana iz svinjske kičmene moždine 1983, i ustanovljeno je da takođe stimuliše intestinalne kontrakcije.[10]
Receptor
urediEndogeni receptor supstance P je neurokininski 1 receptor (NK1-receptor, NK1R).[11] On pripada familiji tahikininskih receptora G protein-spregnutih receptora.[12]
Literatura
uredi- ↑ Li Q, Cheng T, Wang Y, Bryant SH (2010). „PubChem as a public resource for drug discovery.”. Drug Discov Today 15 (23-24): 1052-7. DOI:10.1016/j.drudis.2010.10.003. PMID 20970519.
- ↑ Evan E. Bolton, Yanli Wang, Paul A. Thiessen, Stephen H. Bryant (2008). „Chapter 12 PubChem: Integrated Platform of Small Molecules and Biological Activities”. Annual Reports in Computational Chemistry 4: 217-241. DOI:10.1016/S1574-1400(08)00012-1.
- ↑ Hettne KM, Williams AJ, van Mulligen EM, Kleinjans J, Tkachenko V, Kors JA. (2010). „Automatic vs. manual curation of a multi-source chemical dictionary: the impact on text mining”. J Cheminform 2 (1): 3. DOI:10.1186/1758-2946-2-3. PMID 20331846.
- ↑ Gaulton A, Bellis LJ, Bento AP, Chambers J, Davies M, Hersey A, Light Y, McGlinchey S, Michalovich D, Al-Lazikani B, Overington JP. (2012). „ChEMBL: a large-scale bioactivity database for drug discovery”. Nucleic Acids Res 40 (Database issue): D1100-7. DOI:10.1093/nar/gkr777. PMID 21948594.
- ↑ 5,0 5,1 Harrison S, Geppetti P (June 2001). „Substance p”. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology 33 (6): 555–76. DOI:10.1016/S1357-2725(01)00031-0. PMID 11378438.
- ↑ Datar P, Srivastava S, Coutinho E, Govil G (2004). „Substance P: structure, function, and therapeutics”. Current topics in medicinal chemistry 4 (1): 75–103. DOI:10.2174/1568026043451636. PMID 14754378. Arhivirano iz originala na datum 2009-08-17. Pristupljeno 2021-08-12.
- ↑ Chang MM, Leeman SE, Niall HD (July 1971). „Amino-acid sequence of substance P”. Nature: New Biology 232 (29): 86–7.
- ↑ Leeman SE, Mroz EA (December 1974). „Substance P”. Life Sciences 15 (12): 2033–44. PMID 4613983.
- ↑ V Euler US, Gaddum JH (June 1931). „An unidentified depressor substance in certain tissue extracts”. The Journal of Physiology 72 (1): 74–87. PMC 1403098. PMID 16994201.[mrtav link]
- ↑ Panula P, Hadjiconstantinou M, Yang HY, Costa E (October 1983). „Immunohistochemical localization of bombesin/gastrin-releasing peptide and substance P in primary sensory neurons”. The Journal of Neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 3 (10): 2021–9. PMID 6194276.
- ↑ Gerard NP, Garraway LA, Eddy RL Jr, Shows TB, Iijima H, Paquet JL, Gerard C (November 1991). „Human substance P receptor (NK-1): organization of the gene, chromosome localization, and functional expression of cDNA clones”. Biochemistry 30 (44): 10640–6. DOI:10.1021/bi00108a006. PMID 1657150.
- ↑ Maggi CA (1995). „The mammalian tachykinin receptors”. Gen. Pharmacol. 26 (5): 911–44. DOI:10.1016/0306-3623(94)00292-U. PMID 7557266.
Vanjske veze
uredi- Russell J (14. 09. 2001.). „Neurochemical Substance P is Key to Understanding Pain Process”. Fibromyalgia Library. ProHealth.com. Pristupljeno 01. 11. 2008.