- ↑ Li Q, Cheng T, Wang Y, Bryant SH (2010). „PubChem as a public resource for drug discovery.”. Drug Discov Today 15 (23-24): 1052-7. DOI:10.1016/j.drudis.2010.10.003. PMID 20970519. edit
- ↑ Evan E. Bolton, Yanli Wang, Paul A. Thiessen, Stephen H. Bryant (2008). „Chapter 12 PubChem: Integrated Platform of Small Molecules and Biological Activities”. Annual Reports in Computational Chemistry 4: 217-241. DOI:10.1016/S1574-1400(08)00012-1.
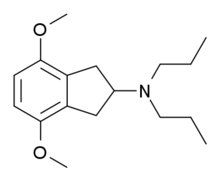
- ↑ Arnerić SP, Long JP, Williams M, et al. (January 1983). „RDS-127 (2-di-n-propylamino-4,7-dimethoxyindane): central effects of a new dopamine receptor agonist”. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 224 (1): 161–70. PMID 6401334.
- ↑ Arnerić SP, Roetker A, Long JP, Mott J, Barfknecht CF (June 1982). „Effects of semirigid methoxamine analogs on vascular smooth muscle: studies of methoxy-2-aminotetralin and 2-aminoindane derivatives”. Archives Internationales De Pharmacodynamie et De Thérapie 257 (2): 263–73. PMID 7114973.
- ↑ Arnerić SP, Long JP (May 1984). „Evidence that a novel dopamine receptor agonist, RDS-127 [2-di-n-propylamino-4,7-dimethoxyindane] has some centrally mediated cardiovascular actions”. The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 36 (5): 318–21. PMID 6145768.
- ↑ Clark JT, Smith ER (1986). „Failure of pimozide and metergoline to antagonize the RDS-127-induced facilitation of ejaculatory behavior”. Physiology & Behavior 37 (1): 47–52. DOI:10.1016/0031-9384(86)90382-3. PMID 3737722.
- ↑ Rezaki YE, Ilhan M (1991). „Evaluation of alpha-adrenoceptor agonistic activity of RDS-127 (2-di-n-propylamino-4,7-dimethoxyindane) in rabbit and rat aortae”. Archives Internationales De Pharmacodynamie et De Thérapie 310: 76–86. PMID 1685313.
- ↑ Sahin I, Ilhan M (1988). „The antimuscarinic activity of a dopamine receptor agonist (RDS-127) differentiates M2-muscarinic receptors of heart, ileum and trachea in guinea-pig”. Archives Internationales De Pharmacodynamie et De Thérapie 296: 163–72. PMID 2907277.
- ↑ Sahin I, Tuncer M, Ilhan M (March 1990). „Dopamine receptor agonists, N,N-dipropyl-2-aminotetralin (TL-68) and 2-di-n-propylamino-4,7-dimethoxyindane (RDS-127) antagonize oxotremorine-induced tremors by antimuscarinic action in mice”. Archives Internationales De Physiologie et De Biochimie 98 (1): 7–9. DOI:10.3109/13813459009115730. PMID 1692697.
- ↑ Arnerić SP, Roetker A, Long JP (September 1982). „Potent anorexic-like effects of RDS-127 (2-di-n-propylamino-4,7-dimethoxyindane) in the rat: a comparison with other dopamine-receptor agonists”. Neuropharmacology 21 (9): 885–90. DOI:10.1016/0028-3908(82)90080-6. PMID 6897285.
- ↑ Kwong LL, Smith ER, Davidson JM, Peroutka SJ (October 1986). „Differential interactions of "prosexual" drugs with 5-hydroxytryptamine1A and alpha 2-adrenergic receptors”. Behavioral Neuroscience 100 (5): 664–8. DOI:10.1037/0735-7044.100.5.664. PMID 2877677.