Rauvolscin
(Preusmjereno sa stranice BLGXFZZNTVWLAY-DIRVCLHFSA-N)
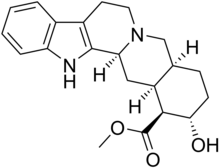
Rauvolscin (izojohimbin, α-johimbin, i korinantidin) je alkaloid koji je prisutan kod više vrsta biljki iz rodova Rauwolfia i Pausinystalia.[5] On je stereoizomer johimbina.[5] Rauvolscin je stimulant centralnog nervnog sistema, lokalni anestetik i u izvesnoj meri afrodizijak.[5]
| |||
| (IUPAC) ime | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| metil estar 17α-hidroksi-20α-johimban-16β-karboksilne kiseline | |||
| Klinički podaci | |||
| Identifikatori | |||
| CAS broj | 131-03-3 6211-32-1 (HCl) | ||
| ATC kod | nije dodeljen | ||
| PubChem[1][2] | 643606 | ||
| ChemSpider[3] | 558737 | ||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:48562 | ||
| ChEMBL[4] | CHEMBL10347 | ||
| Hemijski podaci | |||
| Formula | C21H26N2O3 | ||
| Mol. masa | 354,44 g/mol | ||
| |||
| Farmakoinformacioni podaci | |||
| Trudnoća | ? | ||
| Pravni status | Nije kontrolisan | ||
| Način primene | Oralno | ||
Rauvolscin deluje predominantno kao antagonist α2-adrenergičnog receptora.[6] On takođe deluje kao parcijalni agonist 5-HT1A receptora i antagonist 5-HT2A i 5-HT2B receptora.[7][8][9]
Reference
uredi- ↑ Li Q, Cheng T, Wang Y, Bryant SH (2010). „PubChem as a public resource for drug discovery.”. Drug Discov Today 15 (23-24): 1052-7. DOI:10.1016/j.drudis.2010.10.003. PMID 20970519.
- ↑ Evan E. Bolton, Yanli Wang, Paul A. Thiessen, Stephen H. Bryant (2008). „Chapter 12 PubChem: Integrated Platform of Small Molecules and Biological Activities”. Annual Reports in Computational Chemistry 4: 217-241. DOI:10.1016/S1574-1400(08)00012-1.
- ↑ Hettne KM, Williams AJ, van Mulligen EM, Kleinjans J, Tkachenko V, Kors JA. (2010). „Automatic vs. manual curation of a multi-source chemical dictionary: the impact on text mining”. J Cheminform 2 (1): 3. DOI:10.1186/1758-2946-2-3. PMID 20331846.
- ↑ Gaulton A, Bellis LJ, Bento AP, Chambers J, Davies M, Hersey A, Light Y, McGlinchey S, Michalovich D, Al-Lazikani B, Overington JP. (2012). „ChEMBL: a large-scale bioactivity database for drug discovery”. Nucleic Acids Res 40 (Database issue): D1100-7. DOI:10.1093/nar/gkr777. PMID 21948594.
- ↑ 5,0 5,1 5,2 KOHLI JD, DE NN (June 1956). „Pharmacological action of rauwolscine”. Nature 177 (4521): 1182. DOI:10.1038/1771182a0. PMID 13334509.
- ↑ Perry BD, U'Prichard DC (December 1981). „[3H]rauwolscine (alpha-yohimbine): a specific antagonist radioligand for brain alpha 2-adrenergic receptors”. European Journal of Pharmacology 76 (4): 461–4. DOI:10.1016/0014-2999(81)90123-0. PMID 6276200.
- ↑ Arthur JM, Casañas SJ, Raymond JR (June 1993). „Partial agonist properties of rauwolscine and yohimbine for the inhibition of adenylyl cyclase by recombinant human 5-HT1A receptors”. Biochemical Pharmacology 45 (11): 2337–41. DOI:10.1016/0006-2952(93)90208-E. PMID 8517875.
- ↑ Kaumann AJ (June 1983). „Yohimbine and rauwolscine inhibit 5-hydroxytryptamine-induced contraction of large coronary arteries of calf through blockade of 5 HT2 receptors”. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology 323 (2): 149–54. DOI:10.1007/BF00634263. PMID 6136920.
- ↑ Wainscott DB, Sasso DA, Kursar JD, Baez M, Lucaites VL, Nelson DL (January 1998). „[3HRauwolscine: an antagonist radioligand for the cloned human 5-hydroxytryptamine2b (5-HT2B) receptor”]. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology 357 (1): 17–24. DOI:10.1007/PL00005133. PMID 9459568.