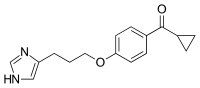
Ciproksifan
Ciproksifan je veoma potentan histaminski H3 inverzni agonist/antagonist.
| |||
| (IUPAC) ime | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ciklopropil 4-(3-(1H-imidazol-4-il)propiloksi)fenil keton | |||
| Klinički podaci | |||
| Identifikatori | |||
| CAS broj | 184025-19-2 | ||
| ATC kod | nije dodeljen | ||
| PubChem[1][2] | 6422124 | ||
| ChEMBL[3] | CHEMBL14638 | ||
| Hemijski podaci | |||
| Formula | C16H18N2O2 | ||
| Mol. masa | 270,33 | ||
| SMILES | eMolekuli & PubHem | ||
| |||
| Farmakoinformacioni podaci | |||
| Trudnoća | ? | ||
| Pravni status | |||
Histaminski H3 receptor je inhibitorni autoreceptor lociran na histaminergičkim nervnim terminalima, i učestvuje u modulaciji otpuštanja histamina u mozgu. Histamin ima pobuđivačko dejstvo na mozak putem H1 receptora u moždanoj kori, tako da lekovi poput ciproksifana koji blokiraju H3 receptor i konsekventno omogućavaju više histamina da bude otpušteno povećavaju budnost.[4][5][6]
Ciproksifan proizvodi budnost i predustretljivost u životinjskim studijama, posledica čega je poboljšana spoznaja bez znatnih stimulacionih efekata pri niskim nivoima zauzeća receptora, i naglašena budnost na višim dozama.[7] Predloženo je da on može da služi kao potencijalni tretman za poremećaje spavanja, kao što su narkolepsija, i za poboljšanje pažnje kod starih osoba, posebno pri tretiranju oboljenje kao što je Alchajmerova bolest.[8][9] On takođe pojačava dejstvo antipsihotičkih lekova, te se smatra da može da bude koristan kao komponenta tretmana šizofrenije.[10]
Reference uredi
- ↑ Li Q, Cheng T, Wang Y, Bryant SH (2010). „PubChem as a public resource for drug discovery.”. Drug Discov Today 15 (23-24): 1052-7. DOI:10.1016/j.drudis.2010.10.003. PMID 20970519.
- ↑ Evan E. Bolton, Yanli Wang, Paul A. Thiessen, Stephen H. Bryant (2008). „Chapter 12 PubChem: Integrated Platform of Small Molecules and Biological Activities”. Annual Reports in Computational Chemistry 4: 217-241. DOI:10.1016/S1574-1400(08)00012-1.
- ↑ Gaulton A, Bellis LJ, Bento AP, Chambers J, Davies M, Hersey A, Light Y, McGlinchey S, Michalovich D, Al-Lazikani B, Overington JP. (2012). „ChEMBL: a large-scale bioactivity database for drug discovery”. Nucleic Acids Res 40 (Database issue): D1100-7. DOI:10.1093/nar/gkr777. PMID 21948594.
- ↑ Passani MB, Lin JS, Hancock A, Crochet S, Blandina P (December 2004). „The histamine H3 receptor as a novel therapeutic target for cognitive and sleep disorders”. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 25 (12): 618–25. DOI:10.1016/j.tips.2004.10.003. PMID 15530639.
- ↑ Passani MB, Giannoni P, Bucherelli C, Baldi E, Blandina P (April 2007). „Histamine in the brain: beyond sleep and memory”. Biochem. Pharmacol. 73 (8): 1113–22. DOI:10.1016/j.bcp.2006.12.002. PMID 17241615.
- ↑ Parmentier R, Anaclet C, Guhennec C, Brousseau E, Bricout D, Giboulot T, Bozyczko-Coyne D, Spiegel K, Ohtsu H, Williams M, Lin JS (April 2007). „The brain H3-receptor as a novel therapeutic target for vigilance and sleep-wake disorders”. Biochem. Pharmacol. 73 (8): 1157–71. DOI:10.1016/j.bcp.2007.01.002. PMID 17288995.
- ↑ Le S, Gruner JA, Mathiasen JR, Marino MJ, Schaffhauser H (June 2008). „Correlation between ex vivo receptor occupancy and wake-promoting activity of selective H3 receptor antagonists”. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 325 (3): 902–9. DOI:10.1124/jpet.107.135343. PMID 18305012.
- ↑ LLigneau X, Lin J, Vanni-Mercier G, Jouvet M, Muir JL, Ganellin CR, Stark H, Elz S, Schunack W, Schwartz J (November 1998). „Neurochemical and behavioral effects of ciproxifan, a potent histamine H3-receptor antagonist”. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 287 (2): 658–66. PMID 9808693.
- ↑ Witkin JM, Nelson DL (July 2004). „Selective histamine H3 receptor antagonists for treatment of cognitive deficiencies and other disorders of the central nervous system”. Pharmacol. Ther. 103 (1): 1–20. DOI:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2004.05.001. PMID 15251226.
- ↑ Pillot C, Ortiz J, Héron A, Ridray S, Schwartz JC, Arrang JM (August 2002). „Ciproxifan, a histamine H3-receptor antagonist/inverse agonist, potentiates neurochemical and behavioral effects of haloperidol in the rat”. J. Neurosci. 22 (16): 7272–80. PMID 12177222.